 Near AIIMS Phulwari Sharif Patna
Near AIIMS Phulwari Sharif Patna [email protected]
[email protected] 7369848448
7369848448
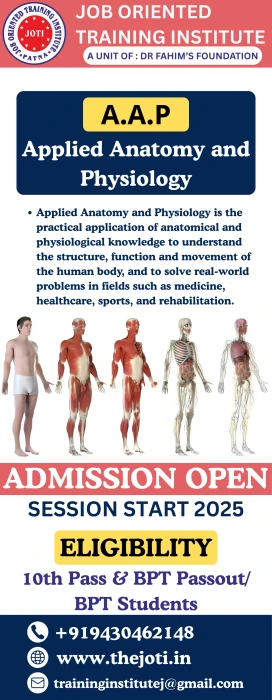
Course Description: This course is designed to provide medical students with a comprehensive understanding of the human body's structure and function, with an emphasis on applying anatomical and physiological knowledge to clinical practice. Course Outline: Module 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology - Overview of anatomy and physiology - Importance of anatomy and physiology in medicine - Basic concepts and terminology Module 2: Musculoskeletal System - Bones and joints - Muscles and movements - Anatomy and physiology of the musculoskeletal system - Clinical applications and case studies Module 3: Nervous System - Brain and spinal cord - Nerves and sensory systems - Anatomy and physiology of the nervous system - Clinical applications and case studies Module 4: Circulatory System - Heart and blood vessels - Blood pressure and circulation - Anatomy and physiology of the circulatory system - Clinical applications and case studies Module 5: Respiratory System - Lungs and airways - Breathing mechanisms and respiration - Anatomy and physiology of the respiratory system - Clinical applications and case studies Module 6: Digestive System - Mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine - Anatomy and physiology of the digestive system - Clinical applications and case studies Module 7: Integumentary System - Skin, hair, nails, and related glands - Anatomy and physiology of the integumentary system - Clinical applications and case studies Module 8: Applied Anatomy and Physiology - Case studies and clinical applications - Integration of anatomical and physiological knowledge - Problem-solving and critical thinking Assessment: - Written exams (40%) - Practical exams (30%) - Group projects and presentations (20%) - Clinical case studies and discussions (10%)

Course Description: This course covers the principles and practices of first aid, including patient assessment, wound management, and treatment of various injuries and illnesses. Course Outline: Module 1: Introduction to First Aid - Definition and importance of first aid - First aid kit and equipment - Patient assessment and triage Module 2: Wound Management - Types of wounds (cuts, lacerations, abrasions, etc.) - Wound cleaning and dressing - Suturing and stapling Module 3: Bleeding and Shock - Types of bleeding (arterial, venous, capillary) - Control of bleeding (tourniquets, pressure points, etc.) - Recognition and treatment of shock Module 4: musculoskeletal Injuries - Sprains and strains - Fractures and dislocations - Head and spine injuries Module 5: Medical Emergencies - Cardiac arrest and CPR - Stroke and TIA - Seizures and epilepsy Module 6: Environmental Injuries - Burns (thermal, electrical, chemical) - Cold-related illnesses (hypothermia, frostbite) - Heat-related illnesses (heat exhaustion, heat stroke) Module 7: Pediatric and Geriatric First Aid - Special considerations for children and older adults - Pediatric and geriatric assessment and treatment Module 8: First Aid in Special Situations - First aid in the wilderness - First aid in mass casualty situations - First aid in disaster response Assessment: - Written exams (40%) - Practical exams (30%) - Group projects and presentations (20%) - Participation and attendance (10%)
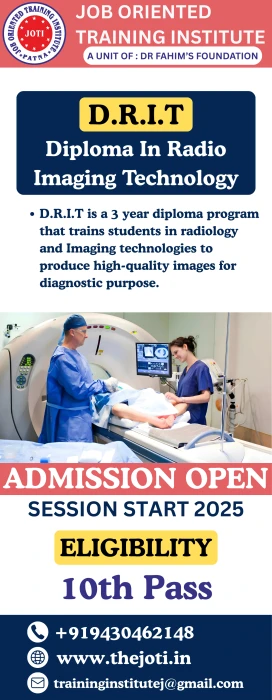
General syllabus for a 3-year program in Diagnostic Radiography and Imaging Technology (DRIT): Year 1: - Semester 1: - Anatomy and Physiology - Physics and Instrumentation - Introduction to Diagnostic Radiography - Radiographic Positioning and Techniques - Semester 2: - Radiographic Imaging and Processing - Radiation Safety and Protection - Patient Care and Management - Medical Ethics and Law Year 2: - Semester 3: - Diagnostic Radiography and Imaging Techniques - Computed Tomography (CT) Scanning - Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Ultrasound and Sonography - Semester 4: - Radiation Therapy and Oncology - Nuclear Medicine and PET Imaging - Mammography and Breast Imaging - Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiology Year 3: - Semester 5: - Advanced Diagnostic Radiography and Imaging Techniques - Research Methods and Biostatistics - Quality Assurance and Quality Control - Healthcare Management and Administration - Semester 6: - Project Work/Dissertation - Clinical Practicum and Internship - Continuing Education and Professional Development Note that this is just a general outline, and the specific syllabus may vary depending on the institution and program. Additionally, some programs may have varying durations, such as 2 years or 4 years. It's always best to check with the institution for the most up-to-date and accurate information.
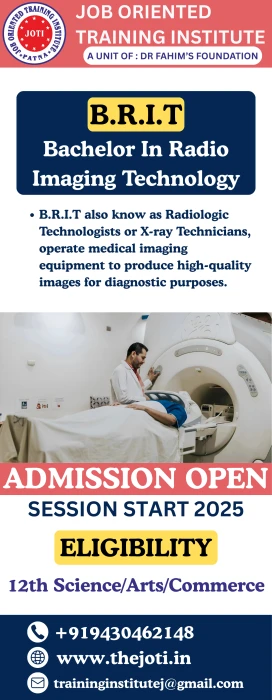
Here is a general syllabus for a 3-year Bachelor of Radiology and Imaging Technology program: Year 1: - Semester 1: - Introduction to Radiology and Imaging Technology - Human Anatomy and Physiology - Radiation Physics and Safety - Imaging Techniques and Procedures - Radiological Equipment and Maintenance - Semester 2: - Radiography and Imaging Principles - Patient Care and Communication - Radiation Protection and Safety - Imaging Modalities (X-ray, CT, MRI) - Medical Ethics and Law Year 2: - Semester 3: - Advanced Radiography and Imaging Techniques - Cross-Sectional Anatomy - Imaging Pathology and Disease Processes - Radiopharmacology and Contrast Media - Research Methodology and Biostatistics - Semester 4: - CT Scanning and Imaging - MRI and Spectroscopy - Ultrasound and Doppler Imaging - Nuclear Medicine and PET Imaging - Quality Control and Quality Assurance Year 3: - Semester 5: - Advanced Imaging Modalities (Mammography, Fluoroscopy) - Interventional Radiology and Procedures - Radiation Therapy and Oncology - Imaging Informatics and PACS - Healthcare Management and Administration - Semester 6: - Project Work/Dissertation - Viva Voce - Clinical Internship/Practicum Electives (choose one): - Cardiovascular Imaging - Neuroradiology - Musculoskeletal Imaging - Pediatric Imaging - Healthcare Informatics Practical Training: - Students will undergo practical training in various radiology and imaging departments, including X-ray, CT, MRI, and ultrasound. Internship: - Students will undergo a 6-month internship in a hospital or imaging center, where they will gain hands-on experience in radiology and imaging technology. Note: The syllabus may vary depending on the institution and country. This is just a general outline.

A Bachelor of Vocation (B.Voc) in Medical Laboratory Technology (MLT) is a three-year undergraduate program that focuses on practical, skill-based training in diagnostic laboratory sciences. The curriculum emphasizes hands-on experience, preparing students for immediate employment in the healthcare industry upon graduation. Course structure and exit options The B.Voc program is aligned with the University Grants Commission's (UGC) National Skills Qualifications Framework (NSQF) and features multiple exit points. Exit after 1 year: Earn a Diploma in Medical Laboratory Technology. Exit after 2 years: Earn an Advanced Diploma in Medical Laboratory Technology. Complete 3 years: Receive the Bachelor of Vocation (B.Voc) degree in Medical Laboratory Technology. Key subjects covered Throughout the program, students gain expertise in a variety of diagnostic and laboratory techniques. Core subjects: Biochemistry, Hematology, Microbiology, Immunology, Histopathology, and Clinical Pathology. Practical skills: Phlebotomy (blood sample collection), handling advanced laboratory equipment, and ensuring quality control. Professional training: Laboratory management, medical ethics, patient safety, and communication skills. Eligibility criteria While requirements can vary by institution, general eligibility for a B.Voc in MLT typically includes: Completion of 10+2 (or equivalent) from a recognized board. Most institutions require a Science stream with Physics, Chemistry, and Biology (PCB), with minimum marks (often 50%). Some institutions may offer flexibility for students from other streams who demonstrate an aptitude for the field. Career scope and job opportunities Graduates of a B.Voc in MLT have strong employability in the healthcare sector, which has a high demand for skilled lab professionals. You can find employment in hospitals, diagnostic labs, research facilities, and blood banks. Common job roles include: Medical Laboratory Technician Blood Bank Technician Research Assistant Laboratory Supervisor or Manager Quality Control Specialist Clinical Research Coordinator Higher education For those interested in further specialization, a B.Voc in MLT also serves as a foundation for postgraduate studies in fields like: M.Sc. Medical Laboratory Technology M.Sc. Clinical Research M.Sc. Microbiology or Biochemistry